Free Practice Questions — Test your knowledge before buying
Get StartedThis free trial page is proudly prepared by the CMFASExam Exam Team.
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
Premium Practice Questions
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
A financial institution acting as a submitter for a surveyed benchmark is reviewing its internal control framework. Which of the following best describes the requirements for auditing and monitoring the benchmark rate setting process?
Correct: The requirement for an annual independent audit or assurance plan ensures that the benchmark rate setting process is scrutinized by a party outside the immediate business unit. These audit outcomes are not submitted automatically but must be ready for the MAS to review if they ask for them.
Incorrect: The suggestion that surveillance only covers internal staff is wrong because monitoring must also include communications between different submitting parties to prevent collusion. The claim that product control checks are mandatory every six months for all benchmarks is incorrect; the guidelines suggest considering more frequent checks specifically for surveyed benchmarks rather than setting a rigid semi-annual rule for everyone. The idea that reports must be sent automatically to the regulator within a specific thirty-day window is inaccurate, as the standard is to provide them upon request.
Takeaway: Submitters and IDBs must maintain an annual independent audit cycle for benchmark activities and ensure that surveillance covers both internal and inter-party communications.
Correct: The requirement for an annual independent audit or assurance plan ensures that the benchmark rate setting process is scrutinized by a party outside the immediate business unit. These audit outcomes are not submitted automatically but must be ready for the MAS to review if they ask for them.
Incorrect: The suggestion that surveillance only covers internal staff is wrong because monitoring must also include communications between different submitting parties to prevent collusion. The claim that product control checks are mandatory every six months for all benchmarks is incorrect; the guidelines suggest considering more frequent checks specifically for surveyed benchmarks rather than setting a rigid semi-annual rule for everyone. The idea that reports must be sent automatically to the regulator within a specific thirty-day window is inaccurate, as the standard is to provide them upon request.
Takeaway: Submitters and IDBs must maintain an annual independent audit cycle for benchmark activities and ensure that surveillance covers both internal and inter-party communications.
A client enters into a transaction with a bank for a large currency trade. The bank and the client have previously established terms and conditions defining their interaction. Which of the following best describes the bank’s role when it acts as a principal in this transaction?
Correct: Filling the order according to agreed terms and conditions while potentially utilizing own inventory is the right answer because it describes a principal-based relationship where the market participant acts as the counterparty to the client. In this capacity, the participant takes on market risk and manages the execution through its own books or available market liquidity.
Incorrect: The description of executing a trade on behalf of a client for a transparent commission describes an agent capacity, where the participant acts as an intermediary rather than a counterparty. Adding an undisclosed spread to a transaction is a violation of transparency requirements, as all costs and fees should be clearly disclosed to the client. Sharing client order details with others to influence benchmark rates is a form of collusion and a breach of confidentiality, which undermines market integrity.
Takeaway: Market participants must be transparent about whether they are acting as a principal or an agent, as each capacity carries different obligations regarding risk, fees, and execution methods.
Correct: Filling the order according to agreed terms and conditions while potentially utilizing own inventory is the right answer because it describes a principal-based relationship where the market participant acts as the counterparty to the client. In this capacity, the participant takes on market risk and manages the execution through its own books or available market liquidity.
Incorrect: The description of executing a trade on behalf of a client for a transparent commission describes an agent capacity, where the participant acts as an intermediary rather than a counterparty. Adding an undisclosed spread to a transaction is a violation of transparency requirements, as all costs and fees should be clearly disclosed to the client. Sharing client order details with others to influence benchmark rates is a form of collusion and a breach of confidentiality, which undermines market integrity.
Takeaway: Market participants must be transparent about whether they are acting as a principal or an agent, as each capacity carries different obligations regarding risk, fees, and execution methods.
Sarah, a trader at a local bank, is tasked with executing a large sell order for a corporate client. The bank is acting as an agent for this specific transaction. Sarah is concerned about the lack of liquidity in the market and considers entering a few small sell trades early to manage the risk. What is the most appropriate course of action for Sarah regarding pre-hedging?
Correct: Refraining from pre-hedging the order is the right action because market participants are strictly prohibited from pre-hedging when acting as an agent. Pre-hedging is defined as the management of risk for anticipated customer orders and is only permitted when a participant acts as a principal, ensuring the practice is fair and transparent.
Incorrect: The option to proceed with pre-hedging if disclosed is wrong because disclosure does not authorize the practice when acting in an agency capacity. Testing market liquidity through small trades is a form of pre-hedging used in principal transactions, but it is not allowed for agency orders. The idea that pre-hedging is acceptable if it benefits the client is incorrect because the prohibition for agents is absolute regardless of the intended outcome for the customer.
Takeaway: Market participants must distinguish between their roles; pre-hedging is a permissible risk management strategy for principal trades but is strictly forbidden when acting as an agent.
Correct: Refraining from pre-hedging the order is the right action because market participants are strictly prohibited from pre-hedging when acting as an agent. Pre-hedging is defined as the management of risk for anticipated customer orders and is only permitted when a participant acts as a principal, ensuring the practice is fair and transparent.
Incorrect: The option to proceed with pre-hedging if disclosed is wrong because disclosure does not authorize the practice when acting in an agency capacity. Testing market liquidity through small trades is a form of pre-hedging used in principal transactions, but it is not allowed for agency orders. The idea that pre-hedging is acceptable if it benefits the client is incorrect because the prohibition for agents is absolute regardless of the intended outcome for the customer.
Takeaway: Market participants must distinguish between their roles; pre-hedging is a permissible risk management strategy for principal trades but is strictly forbidden when acting as an agent.
A Market Participant is preparing to execute a transaction with a customer involving securities listed on a local exchange, using the firm’s own inventory to fulfill the order. How should this transaction be classified and what is the required regulatory procedure?
Correct: [It is classified as a principal trade and the firm must notify the client that it is acting as the counterparty.] is the right answer because when a financial institution fulfills a client’s order using its own internal inventory rather than matching it with another market participant, it is acting as a principal. In these scenarios, regulatory standards require the firm to clearly disclose its role as the direct counterparty to the customer before the transaction is executed.
Incorrect: The classification as an agency trade is incorrect because an agent acts as an intermediary to facilitate a trade between the client and a third party, which is not the case when the firm uses its own holdings. The suggestion that this is a complex transaction requiring a suitability assessment is wrong because, while suitability is a general requirement for certain products, the specific rule for dealing in listed securities as a principal focuses on the disclosure of the firm’s capacity. The idea that this is an off-market trade requiring regulator approval is also incorrect; while off-market trades have specific internal management approval rules, standard principal trades in listed securities do not require permission from a central bank or regulator.
Takeaway: Market Participants must always disclose to their customers when they are acting as the principal counterparty in a transaction involving exchange-traded securities.
Correct: [It is classified as a principal trade and the firm must notify the client that it is acting as the counterparty.] is the right answer because when a financial institution fulfills a client’s order using its own internal inventory rather than matching it with another market participant, it is acting as a principal. In these scenarios, regulatory standards require the firm to clearly disclose its role as the direct counterparty to the customer before the transaction is executed.
Incorrect: The classification as an agency trade is incorrect because an agent acts as an intermediary to facilitate a trade between the client and a third party, which is not the case when the firm uses its own holdings. The suggestion that this is a complex transaction requiring a suitability assessment is wrong because, while suitability is a general requirement for certain products, the specific rule for dealing in listed securities as a principal focuses on the disclosure of the firm’s capacity. The idea that this is an off-market trade requiring regulator approval is also incorrect; while off-market trades have specific internal management approval rules, standard principal trades in listed securities do not require permission from a central bank or regulator.
Takeaway: Market Participants must always disclose to their customers when they are acting as the principal counterparty in a transaction involving exchange-traded securities.
A financial institution is reviewing its Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and technology risk management framework to ensure resilience against market disruptions. Which of the following statements regarding these controls is NOT correct?
Correct: The statement regarding the use of open source architecture for customer integration is the right answer because it is NOT correct. While technology should be efficient, firms must prioritize security and system integrity; allowing customers to integrate their own software via open source architecture could create significant security vulnerabilities and is not a standard regulatory recommendation.
Incorrect: The statement about treasury operations is wrong because it is actually a true requirement; business continuity plans must be holistic and cover front, middle, and back-office functions to be effective. The statement regarding system capacity is wrong because it is a true principle; firms are required to ensure their systems can handle peak loads to prevent failure during volatile market conditions. The statement about encryption is wrong because it is a true requirement; maintaining data confidentiality through encryption is a fundamental control for protecting sensitive financial information.
Takeaway: Business continuity and technology risk management focus on ensuring operational resilience across all departments and maintaining high standards of data security and system capacity.
Correct: The statement regarding the use of open source architecture for customer integration is the right answer because it is NOT correct. While technology should be efficient, firms must prioritize security and system integrity; allowing customers to integrate their own software via open source architecture could create significant security vulnerabilities and is not a standard regulatory recommendation.
Incorrect: The statement about treasury operations is wrong because it is actually a true requirement; business continuity plans must be holistic and cover front, middle, and back-office functions to be effective. The statement regarding system capacity is wrong because it is a true principle; firms are required to ensure their systems can handle peak loads to prevent failure during volatile market conditions. The statement about encryption is wrong because it is a true requirement; maintaining data confidentiality through encryption is a fundamental control for protecting sensitive financial information.
Takeaway: Business continuity and technology risk management focus on ensuring operational resilience across all departments and maintaining high standards of data security and system capacity.
A licensed representative at a Hong Kong brokerage is reviewing various trading strategies involving complex derivatives and currency pairs. Which of the following activities would be classified as prohibited market practices, such as Price Manipulation or False Trading, under the FMRP guidelines?
I. Executing small, successive purchases of a currency pair on an E-Trading platform to move the market price higher before executing a large sell order.
II. Placing a large sell order for a currency just above an exotic option’s knock-in level while simultaneously placing a buy order just below it to trigger the option.
III. An Inter-Dealer Broker advertising a price that has not been instructed by any counterparty to create a false impression of market depth and liquidity.
IV. Breaking a large client order into smaller transactions throughout the day specifically to mitigate market impact and achieve the best execution price.
Correct: Statement I is correct because it describes a strategy intended to cause artificial price movements by creating a false impression of market demand. Statement II is correct because using offsetting orders to intentionally trigger a knock-in level on an exotic derivative is considered creating artificial price movements inconsistent with market conditions. Statement III is correct because providing quotes without genuine intent to trade, often called flying a price, misleads the market regarding available liquidity.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because breaking down large orders to minimize market impact is a standard, legitimate execution practice aimed at achieving the best result for the client, provided there is no intent to distort price discovery or create a false impression of activity.
Takeaway: Market participants must ensure all orders are entered in good faith for bona fide transactions; any strategy intended to disrupt price discovery or create a false impression of liquidity is prohibited. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because it describes a strategy intended to cause artificial price movements by creating a false impression of market demand. Statement II is correct because using offsetting orders to intentionally trigger a knock-in level on an exotic derivative is considered creating artificial price movements inconsistent with market conditions. Statement III is correct because providing quotes without genuine intent to trade, often called flying a price, misleads the market regarding available liquidity.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because breaking down large orders to minimize market impact is a standard, legitimate execution practice aimed at achieving the best result for the client, provided there is no intent to distort price discovery or create a false impression of activity.
Takeaway: Market participants must ensure all orders are entered in good faith for bona fide transactions; any strategy intended to disrupt price discovery or create a false impression of liquidity is prohibited. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
A licensed representative at a Singapore-based brokerage is handling a significant buy order for a corporate client. Which of the following actions would be considered compliant with the standards for execution and handling of orders?
I. Sharing specific details of a client’s order with a counterparty when it is necessary for the effective execution of that order.
II. Delaying the entry of a client’s order into the market to allow the firm to execute a proprietary trade at a more favorable price.
III. Acting as an intermediary and taking the opposite side of a client’s order to profit from the trade without getting prior consent.
IV. Issuing a price quotation to a market participant that is clearly identified as being for reference purposes rather than a firm bid.
Correct: Statement I is correct because representatives are permitted to disclose order details if the information is required to execute the trade effectively for the client. Statement IV is correct because providing reference prices is acceptable under market conduct rules provided they are clearly labeled to distinguish them from firm, tradable quotes.
Incorrect: Statement II is incorrect because intentionally delaying a client’s order to benefit the firm’s own trading position is a prohibited practice known as front running or withholding. Statement III is incorrect because an intermediary is strictly prohibited from bucketing or taking the opposite side of a client’s trade for profit unless the client has provided consent beforehand.
Takeaway: Professional conduct requires prioritizing client interests by avoiding unauthorized disclosure, preventing front running, and ensuring all non-tradable prices are clearly identified to maintain market integrity. Therefore, statements I and IV are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because representatives are permitted to disclose order details if the information is required to execute the trade effectively for the client. Statement IV is correct because providing reference prices is acceptable under market conduct rules provided they are clearly labeled to distinguish them from firm, tradable quotes.
Incorrect: Statement II is incorrect because intentionally delaying a client’s order to benefit the firm’s own trading position is a prohibited practice known as front running or withholding. Statement III is incorrect because an intermediary is strictly prohibited from bucketing or taking the opposite side of a client’s trade for profit unless the client has provided consent beforehand.
Takeaway: Professional conduct requires prioritizing client interests by avoiding unauthorized disclosure, preventing front running, and ensuring all non-tradable prices are clearly identified to maintain market integrity. Therefore, statements I and IV are correct.
A family office establishes a treasury operation in Singapore to manage its own assets and engage in wholesale OTC financial markets. How is this entity classified according to the regulatory framework for these markets?
Correct: An entity is considered a Market Participant if it conducts business within the financial markets. This specifically includes buy-side entities like family offices running treasury operations, regardless of whether they manage their own wealth or external funds.
Incorrect: The suggestion that managing private wealth leads to an exclusion is incorrect because the classification depends on market engagement rather than the ownership of the assets. The term Representative is reserved for the individuals who act on behalf of the entity, not the entity itself. While the entity might provide liquidity, it is formally classified as a buy-side entity rather than a sell-side entity like a bank or merchant bank.
Takeaway: The definition of a Market Participant encompasses a wide range of entities, including buy-side firms like family offices, that participate in the wholesale financial markets.
Correct: An entity is considered a Market Participant if it conducts business within the financial markets. This specifically includes buy-side entities like family offices running treasury operations, regardless of whether they manage their own wealth or external funds.
Incorrect: The suggestion that managing private wealth leads to an exclusion is incorrect because the classification depends on market engagement rather than the ownership of the assets. The term Representative is reserved for the individuals who act on behalf of the entity, not the entity itself. While the entity might provide liquidity, it is formally classified as a buy-side entity rather than a sell-side entity like a bank or merchant bank.
Takeaway: The definition of a Market Participant encompasses a wide range of entities, including buy-side firms like family offices, that participate in the wholesale financial markets.
A corporate treasurer is looking to manage the firm’s immediate liquidity needs by investing surplus cash for a period of six months. Which market segment and instrument type would be most appropriate for this specific requirement?
Correct: The money market is the correct choice because it is designed for short-term borrowing and lending with maturities of one year or less. Instruments like commercial paper and certificates of deposit are standard tools used in this market to provide liquidity and manage short-term funding needs.
Incorrect: The capital market is unsuitable because it facilitates medium and long-term funding, typically involving maturities that exceed one year. The primary market is incorrect because it relates to the initial origination and issuance of securities to raise capital, which does not align with the goal of investing existing surplus cash for liquidity. The derivatives market is incorrect because, while it can be used for hedging, it is not the primary market for placing short-term cash deposits or lending.
Takeaway: Distinguishing between money and capital markets depends on the maturity of the instruments, with money markets handling terms of one year or less.
Correct: The money market is the correct choice because it is designed for short-term borrowing and lending with maturities of one year or less. Instruments like commercial paper and certificates of deposit are standard tools used in this market to provide liquidity and manage short-term funding needs.
Incorrect: The capital market is unsuitable because it facilitates medium and long-term funding, typically involving maturities that exceed one year. The primary market is incorrect because it relates to the initial origination and issuance of securities to raise capital, which does not align with the goal of investing existing surplus cash for liquidity. The derivatives market is incorrect because, while it can be used for hedging, it is not the primary market for placing short-term cash deposits or lending.
Takeaway: Distinguishing between money and capital markets depends on the maturity of the instruments, with money markets handling terms of one year or less.
Two market participants disagree on the terms of a high-value foreign exchange transaction, resulting in a significant open risk for both parties. According to the recommended practices for handling trade discrepancies, what is the most appropriate immediate course of action?
Correct: Closing out the position immediately is the right answer because it is a recommended risk management practice to mitigate market exposure while a dispute is being resolved. This action is taken as a matter of prudence to prevent further losses and does not imply that either party is admitting liability or that a specific party is at fault.
Incorrect: The suggestion to keep the position open until a final decision is reached is wrong because it exposes both participants to continued market risk and potential financial loss during the resolution period. The idea that a party can unilaterally cancel a trade is incorrect as market integrity requires that trades generally stand once executed, and cancellations typically require mutual agreement between both parties. The claim that a lack of response constitutes acknowledgement is wrong because regulatory standards specify that a counterparty’s silence should not be interpreted as an admission or agreement to the terms of a disputed trade.
Takeaway: When a trade discrepancy leads to a dispute involving open market risk, the position should be closed out immediately to limit exposure without assigning blame to either party.
Correct: Closing out the position immediately is the right answer because it is a recommended risk management practice to mitigate market exposure while a dispute is being resolved. This action is taken as a matter of prudence to prevent further losses and does not imply that either party is admitting liability or that a specific party is at fault.
Incorrect: The suggestion to keep the position open until a final decision is reached is wrong because it exposes both participants to continued market risk and potential financial loss during the resolution period. The idea that a party can unilaterally cancel a trade is incorrect as market integrity requires that trades generally stand once executed, and cancellations typically require mutual agreement between both parties. The claim that a lack of response constitutes acknowledgement is wrong because regulatory standards specify that a counterparty’s silence should not be interpreted as an admission or agreement to the terms of a disputed trade.
Takeaway: When a trade discrepancy leads to a dispute involving open market risk, the position should be closed out immediately to limit exposure without assigning blame to either party.
A licensed representative is reviewing various trading strategies and communication practices to ensure compliance with market integrity standards. Which of the following activities would constitute an offense or a breach of regulatory practices?
I. Executing trades between different accounts under the same control that result in no change in the actual economic ownership of the instruments.
II. Informing a corporate client about an ongoing illegal price manipulation scheme by another firm to assist the client in managing their risk.
III. Arranging artificial transactions between two parties for the specific purpose of concealing a trading position or transferring a loss.
IV. Issuing a market commentary that includes a price forecast which later proves to be inaccurate due to unforeseen global economic shifts.
Correct: Statement I is correct because wash trades, which involve transactions with no change in beneficial ownership or economic value, are prohibited as they create a false impression of market volume. Statement II is correct because disseminating information about illegal transactions is an offense, even if the intent is to warn others, as it can exacerbate artificial market conditions or allow others to exploit the manipulation. Statement III is correct because position parking involves using artificial transactions to conceal positions or transfer profits and losses, which is a deceptive practice that undermines market integrity.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because providing a market forecast based on a genuine analysis of public data is a standard professional activity. It only becomes an offense if the person knows or should have known the statement was false, misleading, or deceptive at the time it was published; an honest but inaccurate prediction is not market misconduct.
Takeaway: Market participants must avoid any activities that create artificial market conditions, including wash trades, position parking, and the dissemination of information regarding illegal market activities. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because wash trades, which involve transactions with no change in beneficial ownership or economic value, are prohibited as they create a false impression of market volume. Statement II is correct because disseminating information about illegal transactions is an offense, even if the intent is to warn others, as it can exacerbate artificial market conditions or allow others to exploit the manipulation. Statement III is correct because position parking involves using artificial transactions to conceal positions or transfer profits and losses, which is a deceptive practice that undermines market integrity.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because providing a market forecast based on a genuine analysis of public data is a standard professional activity. It only becomes an offense if the person knows or should have known the statement was false, misleading, or deceptive at the time it was published; an honest but inaccurate prediction is not market misconduct.
Takeaway: Market participants must avoid any activities that create artificial market conditions, including wash trades, position parking, and the dissemination of information regarding illegal market activities. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
A financial institution in Singapore primarily engages in corporate finance advisory, underwriting of share equity, and mergers and acquisitions. Which regulatory classification best describes this entity based on its governing statute and core business activities?
Correct: Merchant Banks approved under the Monetary Authority of Singapore Act is the right answer because these entities are specifically authorized to conduct fee-based activities like corporate finance, underwriting, and mergers and acquisitions. Unlike other banking categories, they are governed by the Merchant Bank Directives rather than the standard framework of the Banking Act.
Incorrect: Wholesale Banks is wrong because these institutions are licensed under the Banking Act and are characterized by their exclusion from retail Singapore Dollar banking rather than a sole focus on investment banking. Offshore Banks is wrong because they are also Banking Act entities that operate with specific restrictions on resident transactions. Full Banks is wrong because they are licensed to provide the complete range of banking services, including retail operations, which is much broader than the specialized activities of a merchant bank.
Takeaway: Merchant Banks are distinguished from other banking classes by their specific approval under the MAS Act and their focus on corporate advisory and investment banking services.
Correct: Merchant Banks approved under the Monetary Authority of Singapore Act is the right answer because these entities are specifically authorized to conduct fee-based activities like corporate finance, underwriting, and mergers and acquisitions. Unlike other banking categories, they are governed by the Merchant Bank Directives rather than the standard framework of the Banking Act.
Incorrect: Wholesale Banks is wrong because these institutions are licensed under the Banking Act and are characterized by their exclusion from retail Singapore Dollar banking rather than a sole focus on investment banking. Offshore Banks is wrong because they are also Banking Act entities that operate with specific restrictions on resident transactions. Full Banks is wrong because they are licensed to provide the complete range of banking services, including retail operations, which is much broader than the specialized activities of a merchant bank.
Takeaway: Merchant Banks are distinguished from other banking classes by their specific approval under the MAS Act and their focus on corporate advisory and investment banking services.
Regarding the roles and restrictions of financial market participants in Singapore, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Correct: The statement claiming that inter-dealer brokers (IDBs) can act as principals is incorrect. IDBs function as wholesale intermediaries that match buyers and sellers to facilitate price discovery and liquidity. They are explicitly prohibited from acting as a principal or taking their own positions in the FX and money markets.
Incorrect: The statement about finance companies is true because they are legally barred from providing demand deposit accounts accessible by cheque or draft, though they may offer term deposits. The statement regarding investment banks is true because market-making activities require them to maintain a two-way market, which often necessitates taking trading positions and managing the associated risks. The statement about private banking is true as their scope of service includes holistic wealth management, such as estate and tax planning for high-net-worth individuals.
Takeaway: Inter-dealer brokers must remain neutral intermediaries and are not permitted to take principal positions in the FX and money markets.
Correct: The statement claiming that inter-dealer brokers (IDBs) can act as principals is incorrect. IDBs function as wholesale intermediaries that match buyers and sellers to facilitate price discovery and liquidity. They are explicitly prohibited from acting as a principal or taking their own positions in the FX and money markets.
Incorrect: The statement about finance companies is true because they are legally barred from providing demand deposit accounts accessible by cheque or draft, though they may offer term deposits. The statement regarding investment banks is true because market-making activities require them to maintain a two-way market, which often necessitates taking trading positions and managing the associated risks. The statement about private banking is true as their scope of service includes holistic wealth management, such as estate and tax planning for high-net-worth individuals.
Takeaway: Inter-dealer brokers must remain neutral intermediaries and are not permitted to take principal positions in the FX and money markets.
A financial practitioner is planning their long-term professional development and looks to the IBF Standards for guidance. How do these standards primarily support a practitioner’s career progression within the Singapore financial sector?
Correct: Providing a practice-oriented roadmap and a suite of accredited training programs to attain necessary job-role competencies is accurate because the IBF Standards are designed to empower practitioners with a clear path for professional development, covering everything from initial licensing to advanced certification.
Incorrect: The suggestion that IBF acts as a primary regulatory authority for legal enforcement is wrong because IBF is an industry association and accreditation agency, not a statutory regulator. The idea that IBF Standards are government-mandated laws is incorrect because they are competency standards developed by the industry to foster professional excellence. The claim that IBF is a profit-driven entity focused only on entry-level licensing is wrong because it is a not-for-profit organization that supports practitioners across all stages of their careers.
Takeaway: The IBF Standards serve as an industry-led competency framework that provides practitioners with a structured roadmap for professional training and certification in the financial sector.
Correct: Providing a practice-oriented roadmap and a suite of accredited training programs to attain necessary job-role competencies is accurate because the IBF Standards are designed to empower practitioners with a clear path for professional development, covering everything from initial licensing to advanced certification.
Incorrect: The suggestion that IBF acts as a primary regulatory authority for legal enforcement is wrong because IBF is an industry association and accreditation agency, not a statutory regulator. The idea that IBF Standards are government-mandated laws is incorrect because they are competency standards developed by the industry to foster professional excellence. The claim that IBF is a profit-driven entity focused only on entry-level licensing is wrong because it is a not-for-profit organization that supports practitioners across all stages of their careers.
Takeaway: The IBF Standards serve as an industry-led competency framework that provides practitioners with a structured roadmap for professional training and certification in the financial sector.
When determining the valuation (fixing) date for a Non-Deliverable Forward (NDF) transaction based on a known maturity (settlement) date, which rule should a Market Participant apply regarding holiday calendars?
Correct: The rule for determining the valuation date from the maturity date requires using only the local currency holidays and ignoring the settlement currency holidays. This ensures the fixing date falls on a day when the local market is active and able to provide a valid reference rate for the currency being traded.
Incorrect: The suggestion to use both holiday calendars is incorrect because the settlement currency’s holidays only affect the maturity date, not the fixing date calculation. The idea that only the settlement currency holidays matter is wrong because the valuation date is fundamentally linked to the availability of the local market’s reference rate. Using the Singapore calendar exclusively is incorrect as it only applies to specific reference pages like ABSFIX01 and does not serve as the general rule for all NDF fixing date calculations.
Takeaway: When calculating NDF fixing dates from settlement dates, Market Participants must use local currency holidays and exclude settlement currency holidays to ensure a valid valuation.
Correct: The rule for determining the valuation date from the maturity date requires using only the local currency holidays and ignoring the settlement currency holidays. This ensures the fixing date falls on a day when the local market is active and able to provide a valid reference rate for the currency being traded.
Incorrect: The suggestion to use both holiday calendars is incorrect because the settlement currency’s holidays only affect the maturity date, not the fixing date calculation. The idea that only the settlement currency holidays matter is wrong because the valuation date is fundamentally linked to the availability of the local market’s reference rate. Using the Singapore calendar exclusively is incorrect as it only applies to specific reference pages like ABSFIX01 and does not serve as the general rule for all NDF fixing date calculations.
Takeaway: When calculating NDF fixing dates from settlement dates, Market Participants must use local currency holidays and exclude settlement currency holidays to ensure a valid valuation.
A corporate treasurer requests a Market Participant to roll over a maturing forward contract at an off-market rate. Which of the following statements regarding the handling of such transactions and unforeseen market events are correct?
I. The Market Participant must obtain express approval from its own senior management before conducting the transaction.
II. The Market Participant must ensure the customer’s senior management has provided express authorization for the off-market rate.
III. Unrealized losses resulting from the extension should be booked as a credit extension against the customer’s credit lines.
IV. Market convention requires that the exchange rate be adjusted to reflect the extension period for unforeseen holidays.
Correct: Statement I is correct because conducting transactions at off-market rates is a high-risk activity that could be used to hide losses, thus requiring the express approval of the financial institution’s senior management. Statement II is correct because the institution must also verify that the client’s own senior management has authorized the use of off-market rates to ensure transparency and prevent unauthorized trading. Statement III is correct because any unrealized losses arising from such extensions must be formally recognized as a credit exposure and managed within the customer’s existing credit lines.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because the standard market practice for unforeseen holidays is to extend the contract to the next business day without any adjustment to the exchange rate, unless the parties have a specific bilateral agreement that allows for such an adjustment.
Takeaway: Transactions at off-market rates require senior management oversight from both parties and must be treated as credit extensions, while unforeseen holidays generally result in contract extensions without rate changes. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because conducting transactions at off-market rates is a high-risk activity that could be used to hide losses, thus requiring the express approval of the financial institution’s senior management. Statement II is correct because the institution must also verify that the client’s own senior management has authorized the use of off-market rates to ensure transparency and prevent unauthorized trading. Statement III is correct because any unrealized losses arising from such extensions must be formally recognized as a credit exposure and managed within the customer’s existing credit lines.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because the standard market practice for unforeseen holidays is to extend the contract to the next business day without any adjustment to the exchange rate, unless the parties have a specific bilateral agreement that allows for such an adjustment.
Takeaway: Transactions at off-market rates require senior management oversight from both parties and must be treated as credit extensions, while unforeseen holidays generally result in contract extensions without rate changes. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
Sarah is a treasury manager at an approved Merchant Bank in Singapore. A non-resident corporate client, which is not a Market Participant, approaches her to enter into a repurchase agreement involving Singapore Government Securities (SGS) with a transaction value of SGD 500,000. How should Sarah handle this request according to the MAS Directives?
Correct: Declining the request is the right answer because Merchant Banks are permitted to enter into repurchase agreements only when the counterparty is a Market Participant. Unlike Offshore Banks, Merchant Banks do not have an exemption for non-resident clients based on transaction size, meaning the client’s status as a non-Market Participant is the deciding factor.
Incorrect: The suggestion to accept the trade based on the SGD 250,000 threshold is wrong because that specific rule applies only to Offshore Banks, not Merchant Banks. The option regarding residency confirmation is incorrect because Merchant Banks cannot trade with non-residents who are not Market Participants regardless of documentation. The statement that Merchant Banks are prohibited from all repos is false as they can trade with Market Participants.
Takeaway: Merchant Banks are restricted to entering into SGS repurchase agreements only with Market Participants, whereas Offshore Banks have additional flexibility for non-resident transactions above a specific value.
Correct: Declining the request is the right answer because Merchant Banks are permitted to enter into repurchase agreements only when the counterparty is a Market Participant. Unlike Offshore Banks, Merchant Banks do not have an exemption for non-resident clients based on transaction size, meaning the client’s status as a non-Market Participant is the deciding factor.
Incorrect: The suggestion to accept the trade based on the SGD 250,000 threshold is wrong because that specific rule applies only to Offshore Banks, not Merchant Banks. The option regarding residency confirmation is incorrect because Merchant Banks cannot trade with non-residents who are not Market Participants regardless of documentation. The statement that Merchant Banks are prohibited from all repos is false as they can trade with Market Participants.
Takeaway: Merchant Banks are restricted to entering into SGS repurchase agreements only with Market Participants, whereas Offshore Banks have additional flexibility for non-resident transactions above a specific value.
A representative at a financial institution is managing a portfolio that includes Singapore Government Securities (SGS) and various interest rate derivatives. Which of the following statements regarding the market practices and dealer obligations for these instruments are correct?
I. Primary Dealers in the SGS market are required to provide liquidity by quoting two-way prices under all market conditions.
II. Prices for debt securities are typically quoted ‘clean,’ meaning the price excludes any interest that has accrued on the bond.
III. For interest rate options transactions, it is assumed that a simultaneous delta hedge is automatically entered into by default.
IV. Dealers in the SGS market are prohibited from disclosing the transaction size or profit/loss of a counterparty to another dealer.
Correct: Statement I is correct because Primary Dealers have a specific regulatory obligation to provide liquidity to the market by quoting two-way prices under all market conditions. Statement II is correct because the standard market convention for debt securities is to quote prices ‘clean,’ which means the quoted price does not include the interest that has accumulated since the last coupon payment. Statement IV is correct because dealers are strictly required to maintain confidentiality, which includes not disclosing sensitive information like the size of a counterparty’s transaction or their profit and loss to other market participants.
Incorrect: Statement III is incorrect because, for interest rate options transactions, the market convention assumes that a simultaneous delta hedge will NOT be entered into unless the parties specifically state otherwise at the time of the trade.
Takeaway: Understanding the specific liquidity obligations of Primary Dealers and the standard pricing and hedging conventions for different asset classes is essential for maintaining market integrity and avoiding settlement misunderstandings. Therefore, statements I, II and IV are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because Primary Dealers have a specific regulatory obligation to provide liquidity to the market by quoting two-way prices under all market conditions. Statement II is correct because the standard market convention for debt securities is to quote prices ‘clean,’ which means the quoted price does not include the interest that has accumulated since the last coupon payment. Statement IV is correct because dealers are strictly required to maintain confidentiality, which includes not disclosing sensitive information like the size of a counterparty’s transaction or their profit and loss to other market participants.
Incorrect: Statement III is incorrect because, for interest rate options transactions, the market convention assumes that a simultaneous delta hedge will NOT be entered into unless the parties specifically state otherwise at the time of the trade.
Takeaway: Understanding the specific liquidity obligations of Primary Dealers and the standard pricing and hedging conventions for different asset classes is essential for maintaining market integrity and avoiding settlement misunderstandings. Therefore, statements I, II and IV are correct.
A newly appointed representative at a capital markets services firm is reviewing the fit and proper requirements and their ongoing disclosure obligations to their principal. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
I. A person is deemed unsuitable if they have been disqualified from acting in a managerial capacity in any foreign jurisdiction.
II. The MAS considers the passage of time since a failure occurred when deciding whether to revoke a representative’s status.
III. A representative must notify their principal of any change in their residential address or contact details within 14 days.
IV. Financial soundness is assessed by considering whether a person is currently the subject of a bankruptcy petition in any jurisdiction.
Correct: Statement III is correct because it identifies a false requirement; representatives are actually required to notify their principal of any changes to their personal particulars, such as a residential address or contact details, within 7 days of the change, not 14 days.
Incorrect: Statement I is incorrect because it is a factually true statement; the assessment of honesty and reputation specifically includes whether a person has been disqualified from managerial roles in Singapore or any foreign jurisdiction. Statement II is incorrect because it is a factually true statement; the authority considers mitigating factors such as the passage of time and the seriousness of the incident when determining if a failure to meet criteria should result in revocation. Statement IV is incorrect because it is a factually true statement; being the subject of a bankruptcy petition in any jurisdiction is a core component of the assessment of a person’s financial soundness.
Takeaway: Fitness and propriety are evaluated based on honesty, competence, and financial soundness, and representatives must adhere to strict 7-day notification windows for any changes to their personal or business particulars. Therefore, statement III is correct.
Correct: Statement III is correct because it identifies a false requirement; representatives are actually required to notify their principal of any changes to their personal particulars, such as a residential address or contact details, within 7 days of the change, not 14 days.
Incorrect: Statement I is incorrect because it is a factually true statement; the assessment of honesty and reputation specifically includes whether a person has been disqualified from managerial roles in Singapore or any foreign jurisdiction. Statement II is incorrect because it is a factually true statement; the authority considers mitigating factors such as the passage of time and the seriousness of the incident when determining if a failure to meet criteria should result in revocation. Statement IV is incorrect because it is a factually true statement; being the subject of a bankruptcy petition in any jurisdiction is a core component of the assessment of a person’s financial soundness.
Takeaway: Fitness and propriety are evaluated based on honesty, competence, and financial soundness, and representatives must adhere to strict 7-day notification windows for any changes to their personal or business particulars. Therefore, statement III is correct.
Kevin is a research analyst at a financial institution. He is preparing a report on a listed company where his spouse serves as a senior executive. Kevin’s firm is concerned about the potential for perceived conflicts of interest and the impact on their reputation. Which of the following measures or principles should the firm apply?
I. Kevin should be required to obtain formal approval from his superiors before engaging in any personal trading activity.
II. The firm should establish a ‘blackout’ period during which Kevin is prohibited from trading in the shares of his spouse’s company.
III. Kevin is permitted to act for multiple principals simultaneously if he ensures his personal interests are always secondary to clients.
IV. The firm must disclose the conflict to affected parties if it cannot be reasonably avoided or effectively managed.
Correct: Statement I is correct because requiring representatives to obtain formal approval before trading is a recognized method for firms to identify and mitigate potential conflicts of interest. Statement II is correct because implementing blackout periods prevents representatives from trading during sensitive times, such as before the release of research reports, which helps avoid the appearance of impropriety. Statement IV is correct because if a conflict cannot be effectively managed or avoided, the firm is obligated to provide full disclosure to the affected parties so they can make an informed decision on whether to proceed.
Incorrect: Statement III is incorrect because the general rule is that a representative may only act for one principal to prevent divided loyalties and conflicting remuneration structures. Exceptions to this rule are strictly limited to situations involving related corporations or where specific regulatory approval has been obtained, rather than being based on the representative’s personal commitment to client interests.
Takeaway: Managing conflicts of interest requires proactive internal controls like trading approvals and blackout periods, and where these are insufficient, mandatory disclosure to the client is required. Therefore, statements I, II and IV are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because requiring representatives to obtain formal approval before trading is a recognized method for firms to identify and mitigate potential conflicts of interest. Statement II is correct because implementing blackout periods prevents representatives from trading during sensitive times, such as before the release of research reports, which helps avoid the appearance of impropriety. Statement IV is correct because if a conflict cannot be effectively managed or avoided, the firm is obligated to provide full disclosure to the affected parties so they can make an informed decision on whether to proceed.
Incorrect: Statement III is incorrect because the general rule is that a representative may only act for one principal to prevent divided loyalties and conflicting remuneration structures. Exceptions to this rule are strictly limited to situations involving related corporations or where specific regulatory approval has been obtained, rather than being based on the representative’s personal commitment to client interests.
Takeaway: Managing conflicts of interest requires proactive internal controls like trading approvals and blackout periods, and where these are insufficient, mandatory disclosure to the client is required. Therefore, statements I, II and IV are correct.
Sarah is a representative at a financial institution and is reviewing the firm’s personal dealing policy to ensure her family’s trades are compliant. Which of the following individuals is NOT explicitly categorized as a “connected person” under the standard guidelines for personal dealing?
Correct: A cousin living in a separate residence is the right answer because the regulatory guidelines for personal dealing only include relatives as connected persons if they share the same household as the representative.
Incorrect: The dependent step-child is a true statement because the rules specifically include all dependent children and step-children as connected persons regardless of their residence. The individual with a close link is a true statement because the policy extends to any person with whom the representative maintains a close personal or professional connection. The person with a material interest is a true statement because the guidelines cover anyone who has a direct or indirect interest in the outcome of the personal transaction.
Takeaway: To prevent conflicts of interest, personal dealing restrictions apply not only to the representative but also to a defined group of connected persons, including household relatives and those with close personal or financial ties.
Correct: A cousin living in a separate residence is the right answer because the regulatory guidelines for personal dealing only include relatives as connected persons if they share the same household as the representative.
Incorrect: The dependent step-child is a true statement because the rules specifically include all dependent children and step-children as connected persons regardless of their residence. The individual with a close link is a true statement because the policy extends to any person with whom the representative maintains a close personal or professional connection. The person with a material interest is a true statement because the guidelines cover anyone who has a direct or indirect interest in the outcome of the personal transaction.
Takeaway: To prevent conflicts of interest, personal dealing restrictions apply not only to the representative but also to a defined group of connected persons, including household relatives and those with close personal or financial ties.
Sarah, a dealer at a Singapore financial institution, realizes she has a short position in Singapore Government Securities (SGS) and cannot fulfill a delivery obligation on the scheduled value date. She is concerned about the potential for a mandatory buy-in by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). What is the latest Sarah can deliver the securities to avoid receiving a formal buy-in notice?
Correct: Delivering the securities by 1600h on the business day following the original value date is required because this is the final deadline to prevent the issuance of a buy-in notice. If the short position is not covered by this specific time, the regulatory process for a forced buy-in begins on the following business day.
Incorrect: The time of 0915h on the second business day is wrong because this is when the notice is issued, meaning the deadline to avoid it has already passed. The time of 1015h on the second business day is wrong because this is the moment the authority begins purchasing securities to cover the short. The time of 1630h on the business day that the original trade was executed is wrong as it merely represents the close of normal trading hours and does not account for the allowed settlement grace period.
Takeaway: To prevent a mandatory buy-in, short positions in government securities must be settled no later than 1600h on the first business day after the original value date.
Correct: Delivering the securities by 1600h on the business day following the original value date is required because this is the final deadline to prevent the issuance of a buy-in notice. If the short position is not covered by this specific time, the regulatory process for a forced buy-in begins on the following business day.
Incorrect: The time of 0915h on the second business day is wrong because this is when the notice is issued, meaning the deadline to avoid it has already passed. The time of 1015h on the second business day is wrong because this is the moment the authority begins purchasing securities to cover the short. The time of 1630h on the business day that the original trade was executed is wrong as it merely represents the close of normal trading hours and does not account for the allowed settlement grace period.
Takeaway: To prevent a mandatory buy-in, short positions in government securities must be settled no later than 1600h on the first business day after the original value date.
Tan is a relationship manager at a Singapore-based bank. He is reviewing a request from ‘EuroHedge Ltd’, a non-resident hedge fund, and ‘TechCorp Treasury’, a non-resident corporate treasury center, for Singapore Dollar (SGD) credit facilities. Which of the following statements regarding the restrictions on lending SGD to non-resident entities are correct?
I. The bank may lend up to SGD 5 million to EuroHedge Ltd for any purpose, provided the aggregate credit facilities for this borrower do not exceed this limit.
II. The SGD 5 million lending limit does not apply to the credit facility provided to TechCorp Treasury as it is a non-financial institution.
III. If EuroHedge Ltd borrows more than SGD 5 million to be used outside Singapore, the bank must ensure the funds are converted into foreign currency.
IV. The bank is required to submit a report of its aggregate outstanding SGD lending to non-resident financial institutions to the MAS every quarter.
Correct: Statement I is correct because banks are permitted to lend up to SGD 5 million to non-resident financial institutions for any purpose. Statement II is correct because the lending restrictions specifically exclude non-financial institutions, such as corporate treasury centers, from the definition of restricted non-resident entities. Statement III is correct because for any lending exceeding the SGD 5 million limit intended for use outside Singapore, the proceeds must be converted or swapped into a foreign currency.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because the regulatory requirement for licensed market participants is to report aggregate outstanding SGD lending to non-resident financial institutions to the regulator on a monthly basis, not a quarterly basis.
Takeaway: While SGD lending to non-resident financial institutions is generally capped and subject to conversion requirements for larger amounts, these restrictions do not apply to non-financial entities like corporate treasury centers. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
Correct: Statement I is correct because banks are permitted to lend up to SGD 5 million to non-resident financial institutions for any purpose. Statement II is correct because the lending restrictions specifically exclude non-financial institutions, such as corporate treasury centers, from the definition of restricted non-resident entities. Statement III is correct because for any lending exceeding the SGD 5 million limit intended for use outside Singapore, the proceeds must be converted or swapped into a foreign currency.
Incorrect: Statement IV is incorrect because the regulatory requirement for licensed market participants is to report aggregate outstanding SGD lending to non-resident financial institutions to the regulator on a monthly basis, not a quarterly basis.
Takeaway: While SGD lending to non-resident financial institutions is generally capped and subject to conversion requirements for larger amounts, these restrictions do not apply to non-financial entities like corporate treasury centers. Therefore, statements I, II and III are correct.
A Market Participant is reviewing its internal procedures for managing client assets and trust accounts. Which of the following statements regarding the handling of customer money and assets is NOT correct?
Correct: The statement regarding the commingling of customer funds with the firm’s own funds is NOT correct because regulations strictly prohibit mixing client money with the firm’s operational capital. Customer funds must be held in segregated trust accounts to ensure they are protected and used only for the client’s intended purposes.
Incorrect: The statement about pooling different customers’ funds is true; while firm and client funds must be separate, it is permissible to deposit funds from multiple different customers into the same trust account. The statement about interest is true; any interest earned on the customer’s funds must be credited to the customer rather than retained by the firm. The statement about the application of funds is true; firms are legally required to apply customer money solely for the purposes that the customer has specifically agreed to.
Takeaway: Customer funds must always be segregated from the firm’s own money and used strictly for agreed purposes, with any interest earned credited back to the customer.
Correct: The statement regarding the commingling of customer funds with the firm’s own funds is NOT correct because regulations strictly prohibit mixing client money with the firm’s operational capital. Customer funds must be held in segregated trust accounts to ensure they are protected and used only for the client’s intended purposes.
Incorrect: The statement about pooling different customers’ funds is true; while firm and client funds must be separate, it is permissible to deposit funds from multiple different customers into the same trust account. The statement about interest is true; any interest earned on the customer’s funds must be credited to the customer rather than retained by the firm. The statement about the application of funds is true; firms are legally required to apply customer money solely for the purposes that the customer has specifically agreed to.
Takeaway: Customer funds must always be segregated from the firm’s own money and used strictly for agreed purposes, with any interest earned credited back to the customer.
A dealer at a financial institution is managing a large currency hedge for a corporate client. Which of the following statements regarding the handling of confidential information is NOT correct?
Correct: Sharing confidential information with internal colleagues who do not have a valid business reason for receiving it is prohibited, even if those colleagues have signed a non-disclosure agreement. Access must be strictly limited to those who need the information for specific, legitimate purposes to ensure it is not misused or inadvertently leaked.
Incorrect: The statement regarding a bank’s own market positions is true because trading information includes the firm’s own activity and order book, which must be kept confidential. The requirement to obtain management permission before visiting another firm’s dealing room is a true and specific measure designed to prevent the accidental disclosure of sensitive information. The classification of hedging recommendations as trading information is true because the definition includes related information produced by the Market Participant during the course of serving a customer.
Takeaway: Market Participants must ensure that confidential information is only shared with parties who have a valid reason for receiving it and that access is strictly controlled to prevent misuse.
Correct: Sharing confidential information with internal colleagues who do not have a valid business reason for receiving it is prohibited, even if those colleagues have signed a non-disclosure agreement. Access must be strictly limited to those who need the information for specific, legitimate purposes to ensure it is not misused or inadvertently leaked.
Incorrect: The statement regarding a bank’s own market positions is true because trading information includes the firm’s own activity and order book, which must be kept confidential. The requirement to obtain management permission before visiting another firm’s dealing room is a true and specific measure designed to prevent the accidental disclosure of sensitive information. The classification of hedging recommendations as trading information is true because the definition includes related information produced by the Market Participant during the course of serving a customer.
Takeaway: Market Participants must ensure that confidential information is only shared with parties who have a valid reason for receiving it and that access is strictly controlled to prevent misuse.
A trader at a commercial bank receives a firm quote from an Inter-Dealer Broker (IDB) but is later told the IDB cannot substantiate it. The bank’s management determines that holding the IDB to the price is justifiable and decides to proceed with a ‘stuffing’ claim. How should the IDB and the bank proceed with the settlement of this transaction?
Correct: The standard procedure for settling a justified ‘stuffing’ claim is for the Inter-Dealer Broker (IDB) to close the transaction at the next available market price and pay the price difference to the participant via a cheque. This method is preferred because it maintains accountability and transparency in the settlement process.
Incorrect: Insisting that the deal be contracted at the original rate or with the original counterparty is specifically prohibited by market standards to prevent further disruption. An IDB should not take a temporary position to honor a quote, as they are generally restricted from taking positions without a principal to substantiate the price. Settling through a reduction in future brokerage fees is discouraged because it impairs the transparency and documentation of the specific transaction discrepancy.
Takeaway: When a participant holds an IDB to a firm quote they cannot substantiate, the settlement must be handled by paying the price difference via cheque rather than forcing the original contract terms.
Correct: The standard procedure for settling a justified ‘stuffing’ claim is for the Inter-Dealer Broker (IDB) to close the transaction at the next available market price and pay the price difference to the participant via a cheque. This method is preferred because it maintains accountability and transparency in the settlement process.
Incorrect: Insisting that the deal be contracted at the original rate or with the original counterparty is specifically prohibited by market standards to prevent further disruption. An IDB should not take a temporary position to honor a quote, as they are generally restricted from taking positions without a principal to substantiate the price. Settling through a reduction in future brokerage fees is discouraged because it impairs the transparency and documentation of the specific transaction discrepancy.
Takeaway: When a participant holds an IDB to a firm quote they cannot substantiate, the settlement must be handled by paying the price difference via cheque rather than forcing the original contract terms.
A compliance manager at a licensed brokerage discovers that a representative has been forging client signatures on several account opening forms. Based on the reporting requirements for misconduct, which of the following describes the firm’s mandatory obligations?
Correct: The requirement to report the matter to the MAS within 14 days of discovery and also lodge a report with the police is the right answer because forgery is specifically categorized as an offence involving dishonesty. For such serious misconduct, firms are mandated to notify the regulator within the two-week timeframe and involve law enforcement authorities.
Incorrect: The suggestion that the firm has 30 days to report is wrong because the regulatory deadline is strictly 14 days from the date the misconduct is discovered. The claim that police involvement is not required is wrong because the regulations explicitly list forgery as a trigger for a mandatory police report. The suggestion that reporting only occurs if the representative is terminated is wrong because the duty to report to the regulator is based on the discovery of the act, not the final disciplinary action taken.
Takeaway: Misconduct involving criminal elements such as forgery or fraud requires both a report to the MAS within 14 days and a formal report to the police.
Correct: The requirement to report the matter to the MAS within 14 days of discovery and also lodge a report with the police is the right answer because forgery is specifically categorized as an offence involving dishonesty. For such serious misconduct, firms are mandated to notify the regulator within the two-week timeframe and involve law enforcement authorities.
Incorrect: The suggestion that the firm has 30 days to report is wrong because the regulatory deadline is strictly 14 days from the date the misconduct is discovered. The claim that police involvement is not required is wrong because the regulations explicitly list forgery as a trigger for a mandatory police report. The suggestion that reporting only occurs if the representative is terminated is wrong because the duty to report to the regulator is based on the discovery of the act, not the final disciplinary action taken.
Takeaway: Misconduct involving criminal elements such as forgery or fraud requires both a report to the MAS within 14 days and a formal report to the police.
Alex, an Inter-Dealer Broker (IDB), is facilitating a money market transaction where a potential lender, Bank A, has indicated commitment by asking ‘who pays’. Alex has three potential borrowers (Bank B, Bank C, and Bank D) interested at the quoted price. Which of the following statements correctly describe the procedures Alex and the participants should follow?
I. Alex should provide the names of Bank B, Bank C, and Bank D simultaneously to Bank A to expedite the selection process.
II. If Bank A rejects Bank B’s name, Alex must obtain Bank A’s approval before disclosing Bank A’s identity to Bank B for verification.
III. If Bank A discovers it has exceeded its credit limit with Bank B after closing, Bank B should not insist on the original counterparty.
IV. Alex may facilitate a name switch if Bank A and Bank B lack sufficient credit lines, provided proper controls and records are maintained.
Correct: Statement II is correct because when a borrower questions the existence of a lender after being rejected for credit reasons, the broker must obtain the lender’s explicit consent before revealing their identity to the borrower. Statement III is correct because if a credit limit breach is discovered after a deal is closed, the borrower is expected to cooperate by accepting an alternative counterparty if one can be found. Statement IV is correct because name switching is a recognized procedure used specifically to address credit limit insufficiencies between market participants, provided the broker maintains strict oversight and documentation.
Incorrect: Statement I is incorrect because brokers are required to provide counterparty names one at a time. Providing multiple names simultaneously to a lender who has committed to a price is not permitted as it compromises the orderly disclosure process and confidentiality.
Takeaway: Inter-Dealer Brokers must manage name disclosure sequentially and are only permitted to use name switching to resolve credit limit issues while maintaining rigorous internal controls. Therefore, statements II, III and IV are correct.
Correct: Statement II is correct because when a borrower questions the existence of a lender after being rejected for credit reasons, the broker must obtain the lender’s explicit consent before revealing their identity to the borrower. Statement III is correct because if a credit limit breach is discovered after a deal is closed, the borrower is expected to cooperate by accepting an alternative counterparty if one can be found. Statement IV is correct because name switching is a recognized procedure used specifically to address credit limit insufficiencies between market participants, provided the broker maintains strict oversight and documentation.
Incorrect: Statement I is incorrect because brokers are required to provide counterparty names one at a time. Providing multiple names simultaneously to a lender who has committed to a price is not permitted as it compromises the orderly disclosure process and confidentiality.
Takeaway: Inter-Dealer Brokers must manage name disclosure sequentially and are only permitted to use name switching to resolve credit limit issues while maintaining rigorous internal controls. Therefore, statements II, III and IV are correct.
A compliance officer is reviewing the firm’s internal policies regarding the handling of confidential customer data. Which of the following statements regarding the disclosure of such information is NOT correct?
Correct: The statement regarding group sharing is NOT correct because information sharing among branches or subsidiaries within a group must be subject to the same restrictions and controls as those applied to external parties. Being part of the same corporate group does not automatically permit the free flow of confidential customer information.
Incorrect: The statement about garnishee orders is a true statement because disclosures are permitted when necessary for compliance with legal orders served on the Market Participant. The statement about auditors and consultants is a true statement because disclosure is allowed for the operations, risk management, and audit functions of the intermediary. The statement about seeking quotes is a true statement because revealing a client’s identity to another bank during the price discovery process without explicit consent is a breach of confidentiality.
Takeaway: Confidentiality obligations are not relaxed for internal group sharing; all information flows within a group must adhere to the same strict controls as disclosures to external third parties.
Correct: The statement regarding group sharing is NOT correct because information sharing among branches or subsidiaries within a group must be subject to the same restrictions and controls as those applied to external parties. Being part of the same corporate group does not automatically permit the free flow of confidential customer information.
Incorrect: The statement about garnishee orders is a true statement because disclosures are permitted when necessary for compliance with legal orders served on the Market Participant. The statement about auditors and consultants is a true statement because disclosure is allowed for the operations, risk management, and audit functions of the intermediary. The statement about seeking quotes is a true statement because revealing a client’s identity to another bank during the price discovery process without explicit consent is a breach of confidentiality.
Takeaway: Confidentiality obligations are not relaxed for internal group sharing; all information flows within a group must adhere to the same strict controls as disclosures to external third parties.
A dealer at a financial institution is asked by a counterparty to provide ‘market colour’ regarding recent activity in the USD/SGD pair. Which of the following actions would be considered an appropriate and acceptable practice for the dealer?
Correct: Describing recent trading activity by aggregating multiple customer flows and referring to volumes in general terms is the right answer because market colour should be restricted to information that is effectively anonymized and grouped. This allows for transparency regarding the general state of the market without revealing the specific positions or identities of individual participants.
Incorrect: Confirming a client’s identity in response to a counterparty’s question is wrong because market participants must not divulge confidential information even if prompted or if the client’s identity is suspected. Disclosing exact execution rates for a single customer is wrong because flows should only be shared by price range to prevent the derivation of underlying confidential information. Using code names that implicitly link activity to a specific participant is wrong because communications must not include any identifiers that allow others to identify individual customer activity.
Takeaway: Market colour must be shared through aggregated and anonymized data to maintain market efficiency while strictly protecting the confidentiality of individual customer identities and specific trading positions.
Correct: Describing recent trading activity by aggregating multiple customer flows and referring to volumes in general terms is the right answer because market colour should be restricted to information that is effectively anonymized and grouped. This allows for transparency regarding the general state of the market without revealing the specific positions or identities of individual participants.
Incorrect: Confirming a client’s identity in response to a counterparty’s question is wrong because market participants must not divulge confidential information even if prompted or if the client’s identity is suspected. Disclosing exact execution rates for a single customer is wrong because flows should only be shared by price range to prevent the derivation of underlying confidential information. Using code names that implicitly link activity to a specific participant is wrong because communications must not include any identifiers that allow others to identify individual customer activity.
Takeaway: Market colour must be shared through aggregated and anonymized data to maintain market efficiency while strictly protecting the confidentiality of individual customer identities and specific trading positions.
Enter your email to unlock Free Practice Questions Set Two instantly.
We respect your privacy. No spam, ever.
Success! Redirecting…
Choose the plan that fits your timeline and start studying today.



Our study materials include thousands of exam-style questions, detailed explanations, and key study notes — everything you need to pass your CMFAS exam on the first try.
Get Started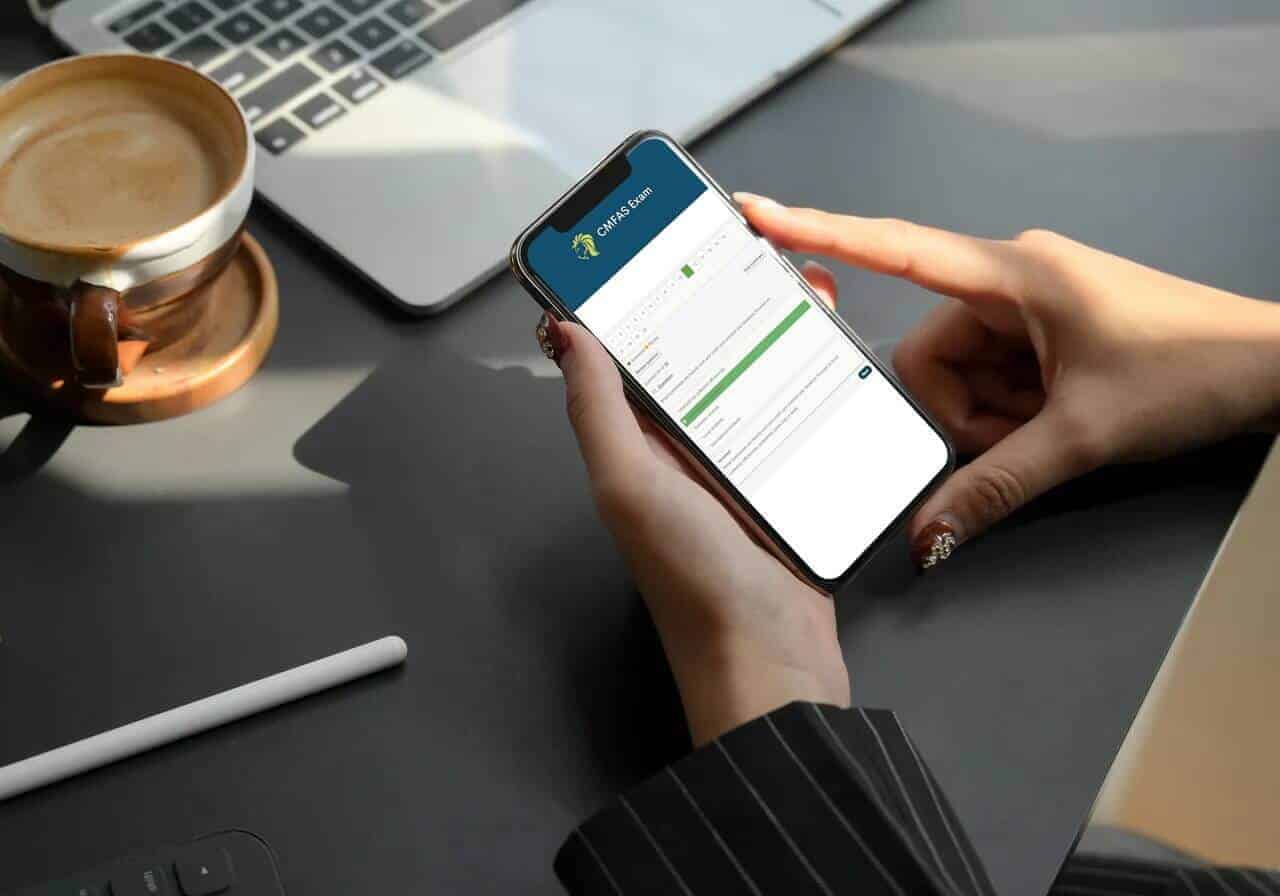
Join thousands of successful candidates who passed their CMFAS exam using our study materials. Our full-time exam team crafts every question to match the real exam format.
Get Started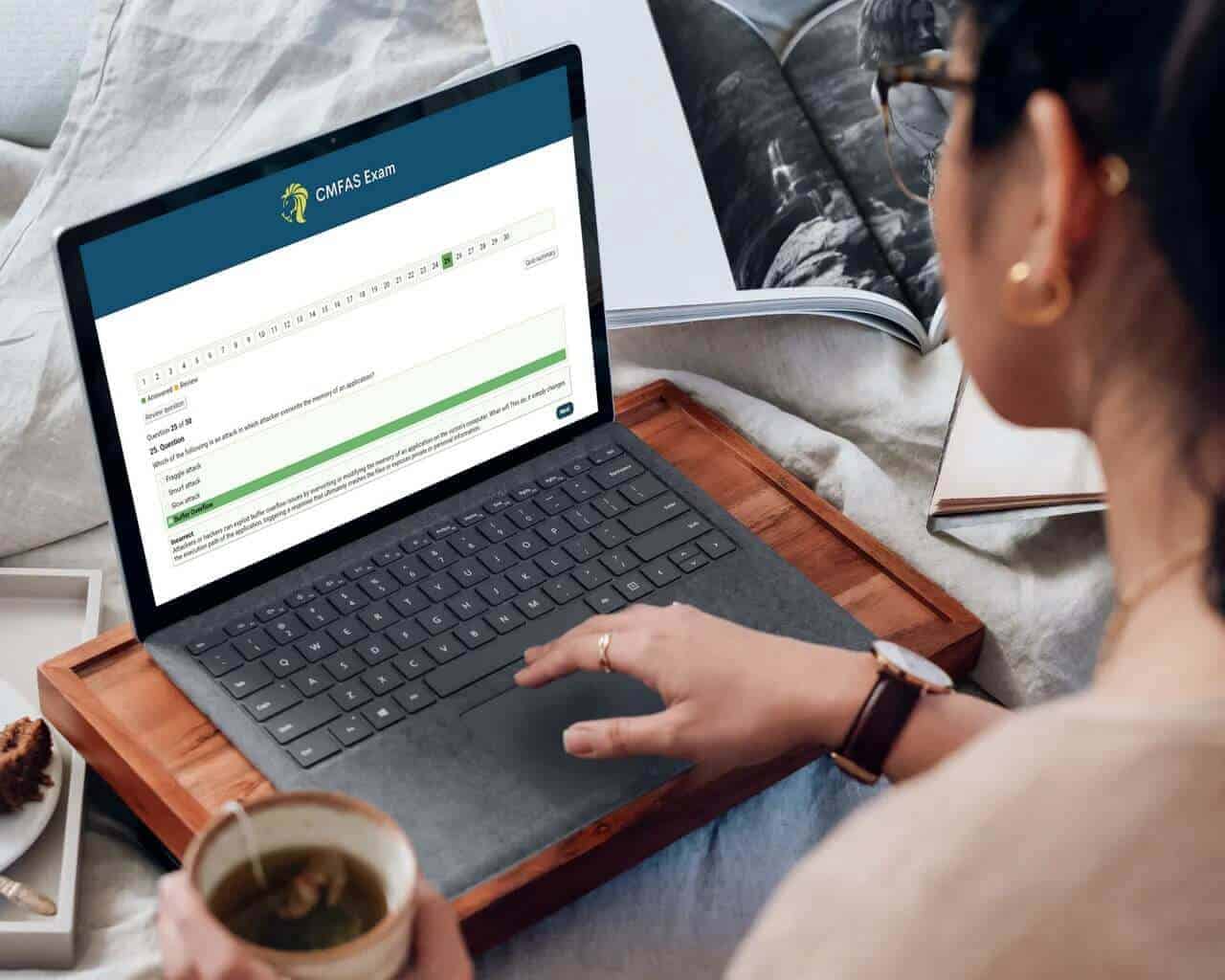
Frequently Updated Practice Questions Bank
Get Started
Without the need to download any mobile apps, you can add our site as an icon on any mobile device or tablet. Study on the go with just one click and continue learning to achieve success.
Get StartedLarge number of questions to help you memorize all possible exam content
Get detailed explanation right after each question
Support all tablets and handheld. Study anywhere
We are very confident with our product. All purchases come with a success guarantee
Get the bonus article of: 17 Secret Tips To Improve CMFAS Study by 39%
All questions adhere to the real examination format to simulate the real exam environment
Our exam bank is frequently updated by our examination team
Each question is carefully crafted by our exam specialist and adheres to the real question formats
No delivery time and fee is needed. Access immediately after payment
See how we stack up against self-study and other prep providers. The choice is clear.
| Feature | CMFASExam | Self-Study | Other Providers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pass RateHistorical first-attempt success | 98.8% | ~50–60% | ~70–80% |
| Question Bank SizeUnique practice questions | Enormous (per module) | Limited / None | Small – Medium |
| Detailed ExplanationsFor every question | ✓ | ✗ | ~ |
| Matches Real Exam FormatUpdated by active test-takers | ✓ | ✗ | ~ |
| Frequently Updated ContentKeeps pace with exam changes | ✓ | ✗ | ~ |
| Key Study NotesCondensed high-yield summaries | ✓ | DIY from manuals | ~ |
| Mobile-FriendlyStudy on any device | ✓ | N/A | ~ |
| "Until You Pass" GuaranteeFree extra access if you fail | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Instant AccessStart in under 60 seconds | ✓ | ✓ | ~ |
| 6 Free BonusesStudy tips, videos, ebooks, tools | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Dedicated Account ManagerIncluded in all plans | ✓ All Plans | ✗ | ~ 1-Year Only |
| Study MindmapVisual overview of key concepts | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| PriceStarting from | SGD$199+ (30 days) | Free – S$50 | USD$199+ |
| Your Time InvestmentAvg. study hours needed | 20–40 hrs | 80–120+ hrs | 40–80 hrs |
| Get Started |
| Feature | RECOMMENDEDCMFASExam | Self-Study | Other Providers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pass Rate | 98.8% | ~50–60% | ~70–80% |
| Question Bank | Enormous | Limited | Small–Med |
| Explanations | ✓ | ✗ | ~ |
| Real Exam Format | ✓ | ✗ | ~ |
| Updated Content | ✓ | ✗ | ~ |
| Study Notes | ✓ | DIY | ~ |
| Mobile-Friendly | ✓ | N/A | ~ |
| Pass Guarantee | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Instant Access | ✓ | ✓ | ~ |
| 6 Free Bonuses | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Acct Manager | ✓ All Plans | ✗ | ~ 1-Yr Only |
| Study Mindmap | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Price From | SGD$199+ | Free–S$50 | USD$199+ |
| Study Hours | 20–40 hrs | 80–120+ hrs | 40–80 hrs |
| Get Started → |
Data based on CMFASExam internal records and candidate feedback. "Other Providers" represents a general market average.
CMFASExam comes with a 100% success guarantee, but we go further than that. We don't just want you to pass; we want you to thrive. Picture your colleagues' faces when they see your new professional title on LinkedIn. Think about how much easier your next promotion will be when you have the credentials to back it up.
We take your career as seriously as you do. That's why we offer a one-year ironclad guarantee. If you don't achieve success, if you don't feel 100% prepared, or even if life got in the way and you didn't have time to study — just let us know.
We will give you a full round of access for free, immediately. No hoops to jump through and no proof required. We've helped over 11,000 candidates leapfrog their competition this year alone without a single refund request. We are so sure you'll be grateful for the results that we're putting our money where our mouth is.
Access enabled immediately as promised after payment, glad that I found your site, ty.
Got no time to prepare the cmfas exam due to my busy day job, thx to cmfas, it helped me pass with ease. happy to provide my compliment to other users.
I am an expat to Singapore and this exam is a headache as I haven't studied any exam for a long while, the service is wonderful and helped me to tackle this licensing exam with ease! thank you very much.
Happy to provide this testimonial for users who are interested in cmfasexam service. I think I have only taken around 50% of the questions they have. good enough for me to pass with high score.
Gladly provide this testimonial and my recommendation to cmfasexam, good value of money if you want to handle this exam as quickly as possible.
Probably the best investment I have ever made passed cmfas exam in one goal.
I am very satisfied with the service CMFASEXAM provided and glad I have enrolled to help me get through the exam.
Big thx guys, passed yesterday M3! for those who are interested to pass cmfas as well, I can recommend CMFASEXAM, practice all their questions twice and you will pass easily.
I am a happy customer from cmfas exam and happy to share their service to my colleagues and friends.
Passed with ease, useful practice questions as promised. Will use your service again in my future cmfas exam.
Promised CS support Emma to provide this testimonial, simply put, I strongly recommend cmfasexam for anyone who wanted to pass the exam easily.
The best thing I like about your service is that questions comes with explanation, it saves me a lot of time to search and find the answers from the study manual.
As a father, time is very limited for me to prepare the exam. Glad I found your service! great job.
Simply awesome service! Questions bank from CMFASEXAM helped me to acquire the licensing qualification seamlessly.
After enabling any module, you will also get 6 bonuses For Free

After you pass, land the job you deserve. This professional guide gives you a competitive edge in your job applications.

20 video lessons on overcoming procrastination, building successful habits, and sustaining the motivation to pass.

Master your focus in a data-driven world. Learn strategies to conquer multitasking pitfalls and maximize memory retention.

Two sets of audio/video study notes (close to 2 hours each) plus visual mind maps that simplify complex concepts at a glance.
Stop drowning in manuals; start mapping your success. Use this Mind Map in high-intensity 25-minute sprints to master the exam faster. Reclaim 67% of your study time through neuro-scientific focus techniques.

Study using a scientifically proven approach. With our built-in Pomodoro study timer, you can monitor your study progress every 25 minutes to improve your efficiency. Research shows this method maximizes results and helps build better memory retention. Save up to 67% of your study time.
Of course you can. Any exam can be prepared for independently. But you'll spend weeks extracting key concepts from dense manuals, guessing which topics are actually tested, and hoping you covered enough.
Or you can let our full-time exam team do that heavy work for you — so you can focus on practice, pass on your first attempt, and spend your evenings with friends and family instead of buried in textbooks.

Everything you need to know before getting started. Still have questions? Email us at [email protected].
It depends on your profession and licensing requirements. We have a comprehensive guide: Everything You Need To Know About CMFAS Exam Before Taking It
If you fail the exam after using our materials, we will grant you an additional round of access (matching the duration you purchased) within 1 year — completely free. Simply email us with your exam result screenshot and we'll process it immediately.
Our full-time exam team crafts unique study materials and quiz banks. Team members attend the actual examination regularly to ensure all content adheres to the recently examined format.
Absolutely. You save money (98.8% pass rate reduces retakes), save time (all materials prepared for you), get fresh content (frequently updated), and no ads — every dollar goes into improving the question bank.
Instantly. Once payment is complete, your account is granted full access immediately. Simply hover over the menu tab that's enabled for your account to start studying.
To respect IBF copyrights, we do not copy the actual examination. Our materials highlight recently examined concepts and familiarize you with the tested content. This builds genuine understanding — far more effective than pure memorization.
Yes. Every single practice question includes a detailed explanation so you understand the underlying rationale immediately after answering.
All materials are digital (online access only). This ensures you always have the latest updated version with no delivery delays. If you prefer offline study, you can print content directly from your browser.
Study time varies, but generally completing over 70% of our question bank will dramatically increase your pass rate. Many candidates study during commutes and breaks.
100% secure. We use Stripe and PayPal for all transactions. No personal information such as name, credit card number, or address is stored by us.
Yes! Purchase two or more modules together and receive an additional 10% discount with 120 days of access. Click here to add multiple modules to your cart.
Students subscribed to the one-year plan get a private tutor program. You can email to ask any questions during the period without limit — personal guidance to ensure you pass.
Yes, we have team purchases! Simply click the Team Purchase option and a 10% discount will be automatically applied to your order.
